Тема: Financial Institutions
Цель урока:
учебная – совершенствование лексических навыков по теме «Financial Institutions»; формирование лексических навыков по текущей теме;
познавательная – понятие об основных финансовых институтах.
Тип урока: комбинированный
- Вопросы по теме «Sources of finance»
- What sources of finance do you know?
- What is the most obvious source of finance? In what way does the company use its own profits?
- What are the sources of finance for a small firm?
- What types of loans do you know?
- For what period of time are short-term loans granted?
- What do you know about overdrafts?
- What can you say about trade credits?
- Do all companies allow to acquire equipment on hire-purchase terms?
- What is the difference between hire-purchase and leasing?
- In what cases do companies prefer obtaining long-terms loans? Are long-terms loans expensive? What does the word "expensive” mean?
- What sources of finance would you use if you had a company?
- Прослушать аудиосюжет к уроку. Ответить на вопросы.
(Start-up, new venture, finance, an angel investor)
1. What is a start-up? What is the synonym to start up? (he builds fence posts)
2. What is financing? What do we finance? (money for start-up)
3. Who is an angel investor? (a person who puts money into the company)
4. How can you find an angel investor? (Most people have business plan)
5. Give a review.
A start-up is a new business. A new business is a new venture. A new venture needs money, or financing. Financing comes from an angel investor.
- Опрос по словам
- Презентация новых слов по теме "Financial institutions”
Перевод дать: банки специализируются на…
What do banks specialize in? Do you agree that banks specialize in
|
Banks specialize in |
supplying short-term loans |
making long-term loans in certain circumstances |
transferring money [trxns'fE:] |
exchanging money |
Перевод дать:
What do insurance companies invest money in?
Is it true that insurance companies invest money in…
In what way do insurance companies get their income?
|
Insurance companies invest money in |
government securities |
company shares |
land |
property of all kinds |
What types of pension funds do you know?
|
Pension funds may be |
state |
private |
|
|
Who contributes to pension funds? Do your parents contribute to any pension fund?
To what pension fund do you parents contribute, state or public?
Are your parents employees, employers, self-employed people?
|
Who contributes to pension funds? |
workers |
employees |
employers |
self-employed people |
Do investments trusts buy shares in other companies which they consider most successful?
Do investments trusts buy shares in other companies which they consider most successful to obtain a profit?
Do investment trusts sell their own shares to the public at large?
Do they pay dividends to people who buy their shares?
Describe the activities of investment trusts.
|
Investment trusts |
buy shares in other companies (these companies are most successful) |
obtain a profit |
sell their own shares |
pay dividends to people who buy their shares. |
Do unit trusts issue shares or units?
Can you resell units of the unit trust on the open market?
Can you sell units back to the unit trust at any time?
|
Unit trusts |
don’t issue shares |
issue units |
cannot resold units on the open market |
can sell units back to the unit trust at any time. |
What schemes do finance houses finance?
Do they pay immediately to a company which sells goods on hire-purchase terms or lease goods?
Do they collect regular instalments from the purchaser?
Describe activities of a finance house?
|
Finance houses |
Finance hire-purchase schemes |
finance leasing schemes |
pay immediately to a company which sells goods on hire-purchase terms or lease goods. |
collect regular installments from the purchaser. |
- Прочитать текст «Financial institutions»
There are many important financial institutions which provide finance for companies. These institutions provide money in different ways.
- Banks
Althouth banks specialize in supplying short-term loans, they are prepared to make loans for longer periods – up to 20 years in certain circumstances.
- Insurance companies
The regular premiums paid by policyholders are invested in government securities, company shares, land, and property of all kinds. The income from these investments makes it possible for insurance companies to pay out interests which are greater than the total payments made by policyholders.
- Pension funds
Although in many countries there is a state pension shceme to which all workers contribute, a large number of employed and self-employed people also belong to private pension schemes. The money which accumulates in these pension funds is invested and works in a very similar manner to the funds of insurance companies.
- Investment trusts
These are limited companies buying shares in other companies which they believe will be the most successful ones. People who then buy shares in investment trusts are paid dividends and investment funds obtain a profit too.
- Unit trusts
These operate in a very similar manner to investment trusts. But they are not limited companies – they do not issue shares, they issue units. These units cannot be re-sold on the open market, but they can be sold back to the unit trust at any time.
- Finance houses
These institutions provide the loans which finance hire-purchase schemes and leasing arrangements. Firms which sell goods on hire-purchase or who lease goods do not have to wait two or three years before their goods are fully paid for. They receive immediate payment from a finance hours, and it is the finance house which collects the regular installments paid by the purchaser.
There are many other specialist financial institutions which provide finance for companies. Besides in many countries a government is an important source of finance for privately-owned firms.
Here is a table
showing sources of funds for industrial and commercial companies in the
|
|
Percentage of total |
|
Internal funds (retained profits) |
64,3 |
|
Issued of ordinary shares |
11,6 |
|
Issue of preference shares |
1,5 |
|
Bank borrowing |
11,4 |
|
Other sources |
11,2 |
|
|
100,0 |
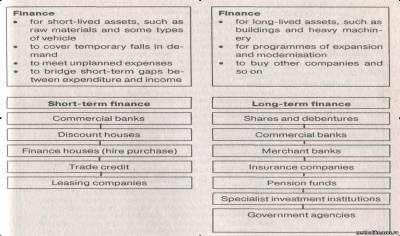
- Рассмотрите диаграмму
Запомните следующие слова:
Short-lived (long-lived) assets – активы с коротким сроком амортизации
Raw materials – сырье
Vehicle ['vi:Ik(q)l] – транспортное средство
Cover temporary falls in demand – покрыть кратковременное падение спроса
To meet unplanned expenses – покрыть незапланированные расходы
To bridge short-term gaps between expenditure and income – покрыть краткосрочный разрыв между расходами и доходами.
Why do people need short-term finance? Long-term finance?
What are sources of short-term finance?
What are sources of long-term finance?